Codetown
Codetown ::: a software developer's community
JavaFX 2.2 Canvas
One of the cool new features of the JavaFX 2.2 developer preview release is a new Canvas node that allows you to do free drawing within an area on the JavaFX scene similar to the HTML 5 Canvas. You can download this release for Windows, Mac, and Linux from JavaFX Developer Preview.
Being adventurous, I decided to take the JavaFX Canvas for a spin around the block. In doing some searching for cool HTML 5 Canvas examples, I came across Dirk Weber's blog comparing performance of HTML5 Canvas, SVG and Adobe Flash,An experiment: Canvas vs. SVG vs. Flash. This looked interesting for a Canvas beginner as I am, so I decided to copy his implementation and see how it runs in JavaFX.
This turned out to be pretty straight forward. Dirk's original JavaScript application for the HTML 5 Canvas contained a spirograph drawn at the top of the screen with 4 sliders beneath it for changing the number of rotations and particles and the inner and outer radius for the spirograph. Also, at the top is a text display showing the frames-per-second after the image is drawn. By manipulating the slider properties, the spirograph is drawn differently and each time the performance is shown in frames per second.
To do the same thing in JavaFX, I first created a JavaFX Application class, with a Stage and Scene and placed the Canvas at the top of the scene with 4 sliders below it followed by a Label to report the frames per second as defined in Dirk's original JavaScript implementation. One change I made to Dirk's implementation was instead of using Arrays of doubles for points, I used the JavaFX Point2D class.
My original goal was just to become familiar with the JavaFX Canvas object, but as I played around I noticed something about the performance. When I ran Dirk's HTML 5 and Flash version I would get a consistent frame-per-second rate of 50-70 fps when I adjusted the sliders (Mac OS X 10.7.4, 2.6 GHz Intel Core 2 Duo, 4 GB ram). However, when I ran my JavaFX version, the first time after starting, it drew the spirograph in the low 40s fps. But I noticed that when I adjusted the sliders, the performance got better. First adjustment, low 80s fps; fifth adjustment, mid 120s; a few more and I was getting 1000 fps, and eventually Infinity fps. I didn't believe the Infinity reading, so I debugged to the code, only to find out that it took less than a millisecond to calculate and draw the spirograph.
I assume that this behavior reflects the Hotspot compiler kicking in after a few iterations of the Spirograph calculation. But, it sure is fast.
The JavaFX source can be downloaded from here:
Notes
Welcome to Codetown!
 Codetown is a social network. It's got blogs, forums, groups, personal pages and more! You might think of Codetown as a funky camper van with lots of compartments for your stuff and a great multimedia system, too! Best of all, Codetown has room for all of your friends.
Codetown is a social network. It's got blogs, forums, groups, personal pages and more! You might think of Codetown as a funky camper van with lots of compartments for your stuff and a great multimedia system, too! Best of all, Codetown has room for all of your friends.
Created by Michael Levin Dec 18, 2008 at 6:56pm. Last updated by Michael Levin May 4, 2018.
Looking for Jobs or Staff?
Check out the Codetown Jobs group.
InfoQ Reading List
DoorDash Builds LLM Conversation Simulator to Test Customer Support Chatbots at Scale
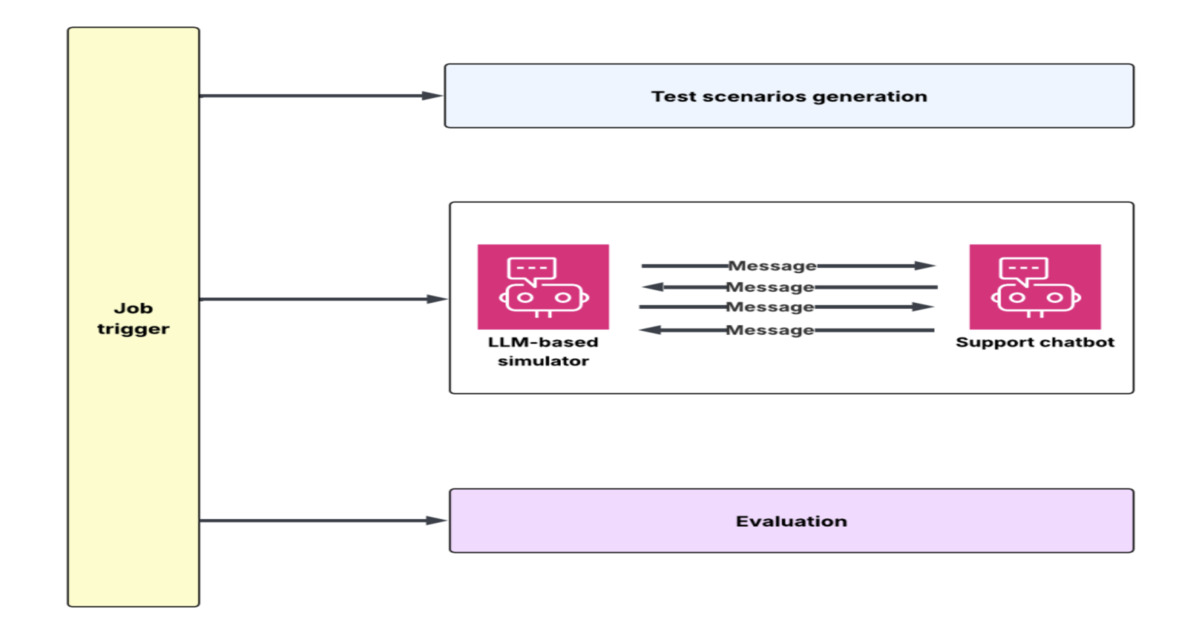
DoorDash engineers built a simulation and evaluation flywheel to test large language model customer support chatbots at scale. The system generates multi-turn synthetic conversations using historical transcripts and backend mocks, evaluates outcomes with an LLM-as-judge framework, and enables rapid iteration on prompts, context, and system design before production deployment.
By Leela KumiliNetflix Uncovers Kernel-Level Bottlenecks While Scaling Containers on Modern CPUs

Engineers at Netflix have uncovered deep performance bottlenecks in container scaling that trace not to Kubernetes or containerd alone, but into the CPU architecture and Linux kernel itself.
By Craig RisiPresentation: Beyond the Code: Hiring for Cultural Alignment

Alicia Collymore discusses the critical role of cultural alignment in building high-performing engineering teams. She explains how to move beyond "vibes" by identifying specific attributes in company values and assessing them during coding challenges and system design sessions. She shares practical advice on using interview debriefs, assessment criteria, and "culture add" to drive growth.
By Alicia CollymoreArticle: The Oil and Water Moment in AI Architecture

Have you ever tried mixing oil and water? That is the moment software architecture is entering as deterministic systems meet non deterministic AI behaviour. Architects must anchor intelligent systems in intent, governance and systems thinking. This article introduces the Architect’s V Impact Canvas, a framework for navigating this shift while keeping human trust at the centre.
By Shweta VohraPodcast: Information Flow: The Hidden Driver of Engineering Culture

In this podcast, Shane Hastie, Lead Editor for Culture & Methods, spoke to Adrian Peryer about Ron Westrum's organizational culture continuum, the role of information flow in shaping team culture, and how leaders can develop requisite imagination to detect weak signals.
By Adrian Peryer
© 2026 Created by Michael Levin.
Powered by
![]()
You need to be a member of Codetown to add comments!
Join Codetown