Codetown
Codetown ::: a software developer's community
Kotlin Thursdays - Image Processing in Kotlin Part 3 with Amanda Hinchman-Dominguez
Kotlin Thursdays: Image Processing in Kotlin Part 3
Part 1: https://codetown.com/group/kotlin/forum/topics/kotlin-thursdays-ima...
Part 2: https://codetown.com/group/kotlin/forum/topics/kotlin-thursdays-ima...
Welcome to Kotlin Thursdays! Last week, we figured out how to write primitive filters and apply them to our images with the or function. This week, we look at refactoring with higher-order functions.
Resources
Think of these resources as supplemental if you happen to be more curious. We always encourage looking into documentation for things you use!
- Project Github Repository: https://github.com/Kotlin-Thursdays/Image-Processing-in-Kotlin
- Installing Java with Oracle: https://www.oracle.com/technetwork/java/javase/downloads/jdk8-downl...
- Kotlin: https://kotlinlang.org/docs/reference/
- TornadoFX: https://edvin.gitbooks.io/tornadofx-guide/content/
Higher Order Functions
We could continue to write individual functions that feeds 2 images and a particular function, but in Kotlin, we have the ability to use a single function that accepts 2 images and a function with the help of higher order functions. Below, you can see how similar our orFilter function and makeDuller function is.
In programming, programs may take data as parameters and pass those parameters into the function to return a different output or alter the behavior of a program. Kotlin is a functional language, and one characteristic of a functional language is that functions are also able to treat functions as data. You can pass a function as a parameter, which is really powerful!
A higher-order function is a function that may take functions as parameters. You can pass a function with double-colon (::). Double-colon (::) is used to get function (callable) reference in Kotlin.
Ruby facilitates higher order functions with yield, which involves passing a block to a method.
Like Ruby, Kotlin treats functions as first-class citizens, which is a pillar of functional programming. In Kotlin, the equivalent of block code is known as lambda functions, indicated by the pattern:
Instead of passing the object as an argument, you invoke the lambda variable as it if were an extension function. Haskell also has higher order functions which can designate the kinds of parameters a function may take within a function.
Implementing applyFilter
In this case, we are going to work with a general function, as opposed to an extension function that is invoked with a qualifer.
The function we write will take a filter function and 2 pixelReaders. Our function parameter, in particular, will only accept functions that take 2 Color parameters and returns a Color.
So here, the input function that accepts the 2 parameters is the receiver type, the output Color receiver object.
fun applyFilter (filter: (Color, Color) --> Color, a: PixelReader, b: PixelReader): PixelWriter {
for (x in 0 until width) {
for (y in 0 until height) {
resultWriter.setColor(x, y, filter(a.getColor(x, y), b.getColor(x, y))
}
}
return resultWriter
}
Conclusion
I hope you all had fun learning a little bit about image processing! Keep exploring and creating new image filters and maybe even as a challenge, think about how you might implement an RGB system to create image filters for colors. Until next time :)
Tags:
Replies to This Discussion
Notes
Welcome to Codetown!
 Codetown is a social network. It's got blogs, forums, groups, personal pages and more! You might think of Codetown as a funky camper van with lots of compartments for your stuff and a great multimedia system, too! Best of all, Codetown has room for all of your friends.
Codetown is a social network. It's got blogs, forums, groups, personal pages and more! You might think of Codetown as a funky camper van with lots of compartments for your stuff and a great multimedia system, too! Best of all, Codetown has room for all of your friends.
Created by Michael Levin Dec 18, 2008 at 6:56pm. Last updated by Michael Levin May 4, 2018.
Looking for Jobs or Staff?
Check out the Codetown Jobs group.
InfoQ Reading List
How Grab Optimizes Image Caching on Android with Time-Aware LRU

To improve image cache management in their Android app, Grab engineers transitioned from a Least Recently Used (LRU) cache to a Time-Aware Least Recently Used (TLRU) cache, enabling them to reclaim storage more effectively without degrading user experience or increasing server costs.
By Sergio De SimoneGoogle Researchers Propose Bayesian Teaching Method for Large Language Models
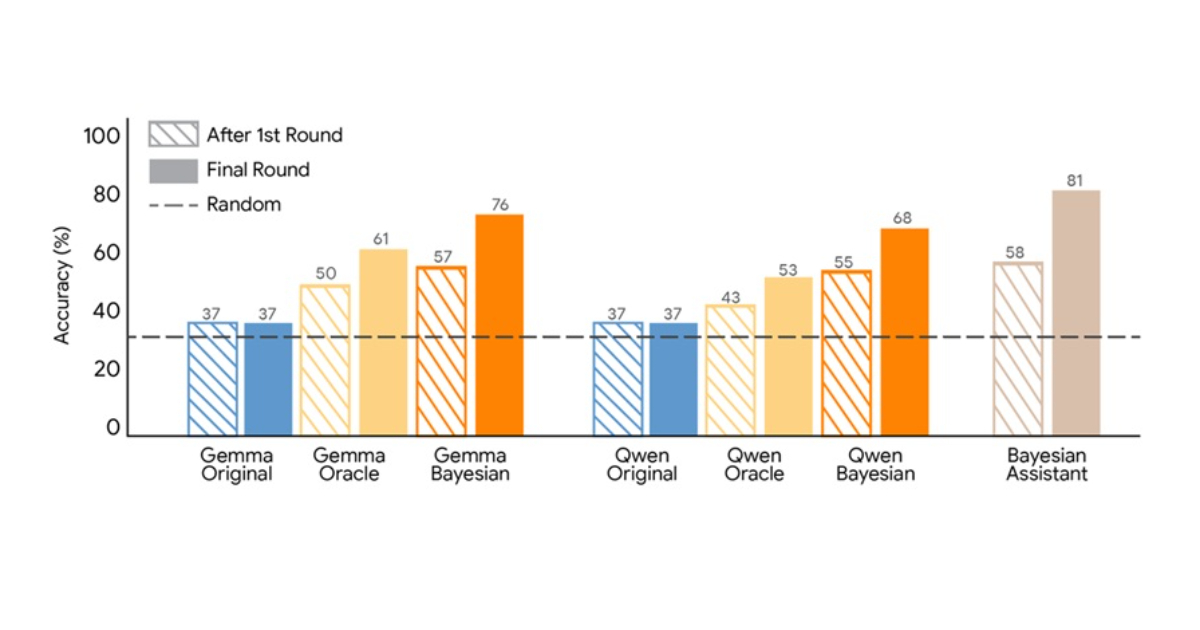
Google Research has proposed a training method that teaches large language models to approximate Bayesian reasoning by learning from the predictions of an optimal Bayesian system. The approach focuses on improving how models update beliefs as they receive new information during multi-step interactions.
By Daniel DominguezCloudflare Introduces Support for ASPA, an Emerging Internet Routing Security Standard

Cloudflare recently announced support for ASPA (Autonomous System Provider Authorization). The new cryptographic standard helps make Internet routing safer by verifying the path data takes across networks to reach its destination and preventing traffic from traversing unreliable or untrusted networks.
By Renato LosioDoorDash Builds LLM Conversation Simulator to Test Customer Support Chatbots at Scale
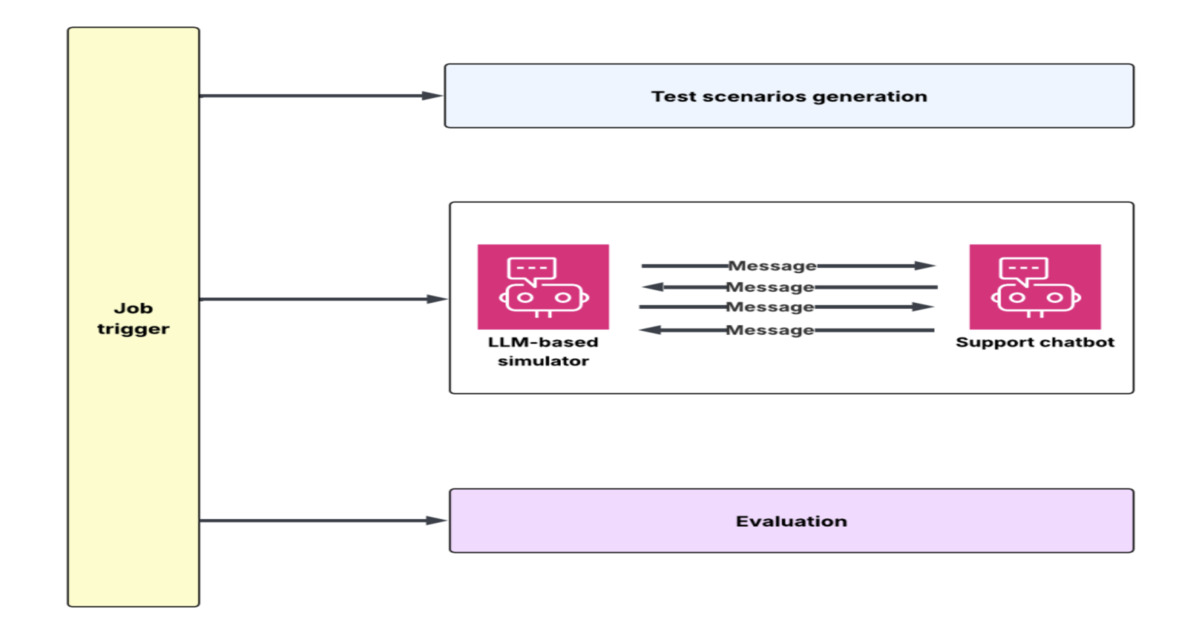
DoorDash engineers built a simulation and evaluation flywheel to test large language model customer support chatbots at scale. The system generates multi-turn synthetic conversations using historical transcripts and backend mocks, evaluates outcomes with an LLM-as-judge framework, and enables rapid iteration on prompts, context, and system design before production deployment.
By Leela KumiliNetflix Uncovers Kernel-Level Bottlenecks While Scaling Containers on Modern CPUs

Engineers at Netflix have uncovered deep performance bottlenecks in container scaling that trace not to Kubernetes or containerd alone, but into the CPU architecture and Linux kernel itself.
By Craig Risi
© 2026 Created by Michael Levin.
Powered by
![]()