Codetown
Codetown ::: a software developer's community
Kotlin Thursdays - Image Processing in Kotlin Part 2 with Amanda Hinchman-Dominguez
Kotlin Thursdays: Image Processing in Kotlin Part 2
Welcome to Kotlin Thursdays! Last week, we were able to render an image with TornadoFX and even manipulate its pixels. Today, we will go over Pixel Math!
Resources
Think of these resources as supplemental if you happen to be more curious. We always encourage looking into documentation for things you use!
- Project Github Repository: https://github.com/Kotlin-Thursdays/Image-Processing-in-Kotlin
- Installing Java with Oracle: https://www.oracle.com/technetwork/java/javase/downloads/jdk8-downl...
- Kotlin: https://kotlinlang.org/docs/reference/
- TornadoFX: https://edvin.gitbooks.io/tornadofx-guide/content/
Topics covered:
- Getting set up with TornadoFX
- Rendering an image and making it duller
- Pixel math!
- Creating image processing filters
- Further considerations with "Big O"
Binary Operations
Last week, we got the hang of how to grab these pixels and do something with them. Today, we're going to expand by creating our own filters using operational pixel manipulation.
For all practical purposes, we're going to be talking about monochromatic images. If we try to write filters using colored pixels, it will prove a lot more difficult to work with RGB values as opposed to just black or white.
Best we learn to walk before we start trying to fly!
In order to create our own image filters, we need to have a solid understanding of pixel math, or binary operations.
Binary operations are the bread and butter of computers! You can compute operations on binary values 1 and 0.
AND - both inputs must be true for the output to be true
0 && 0 = 0
0 && 1 = 0
1 && 0 = 0
1 && 1 = 1
OR - one or both inputs must be true for the output to be true
0 || 0 = 0
0 || 1 = 1
1 || 0 = 1
1 || 1 = 1
NOT - inverse result
!0 = 1
!1 = 0
!(0 && 0) = 1
!(1 || 1) = 0
Likewise, if we assign the color BLACK to 1 and the color WHITE to 0, we can easily apply binary operations to to the binary values black and white. Working with colors gets significantly more difficult when there are RGB values to consider. There are other binary operations like XANDS, XORS, and XNORS, but for now, let's just focus on the first three.
Implementing Primitive Filters
Now that we understand how OR, AND, and NOT works, let's implement these functions with colors.
fun or (a: Color, b: Color) {
return if (a == Color.BLACK || b == Color.BLACK) {
Color.BLACK
}
else { Color.WHITE
}
fun and (a: Color, b: Color) {
return if (a == Color.BLACK && b == Color.BLACK) {
Color.BLACK
} else {
Color.WHITE
}
}
fun not (color: Color) {
return if (color == Color.BLACK) Color.WHITE else Color.BLACK
}
Conclusion
You'll notice that these functions are for pixel colors only. Next week, we look into higher-order functions in Kotlin to learn how we can pass functions as a parameter - but you'll welcome to check out the video to see how we can apply one of these primitive filters to our images! See you next week :)
Tags:
Replies to This Discussion
Notes
Welcome to Codetown!
 Codetown is a social network. It's got blogs, forums, groups, personal pages and more! You might think of Codetown as a funky camper van with lots of compartments for your stuff and a great multimedia system, too! Best of all, Codetown has room for all of your friends.
Codetown is a social network. It's got blogs, forums, groups, personal pages and more! You might think of Codetown as a funky camper van with lots of compartments for your stuff and a great multimedia system, too! Best of all, Codetown has room for all of your friends.
Created by Michael Levin Dec 18, 2008 at 6:56pm. Last updated by Michael Levin May 4, 2018.
Looking for Jobs or Staff?
Check out the Codetown Jobs group.
InfoQ Reading List
Presentation: Beyond the Warehouse: Why BigQuery Alone Won’t Solve Your Data Problems

Sarah Usher discusses the architectural "breaking point" where warehouses like BigQuery struggle with latency and cost. She explains the necessity of a conceptual data lifecycle (Raw, Curated, Use Case) to regain control over lineage and innovation. She shares practical strategies to design a single source of truth that empowers both ML teams and analytics without bottlenecking scale.
By Sarah UsherJava Explores Carrier Classes to Extend Data-Oriented Programming Beyond Records

The OpenJDK Amber project has published a new design note proposing “carrier classes” and “carrier interfaces” to extend record-style data modeling to more Java types. The proposal preserves concise state descriptions, derived methods, and pattern matching, while relaxing structural constraints that limit records.
By A N M Bazlur RahmanVercel Introduces Skills.sh, an Open Ecosystem for Agent Commands
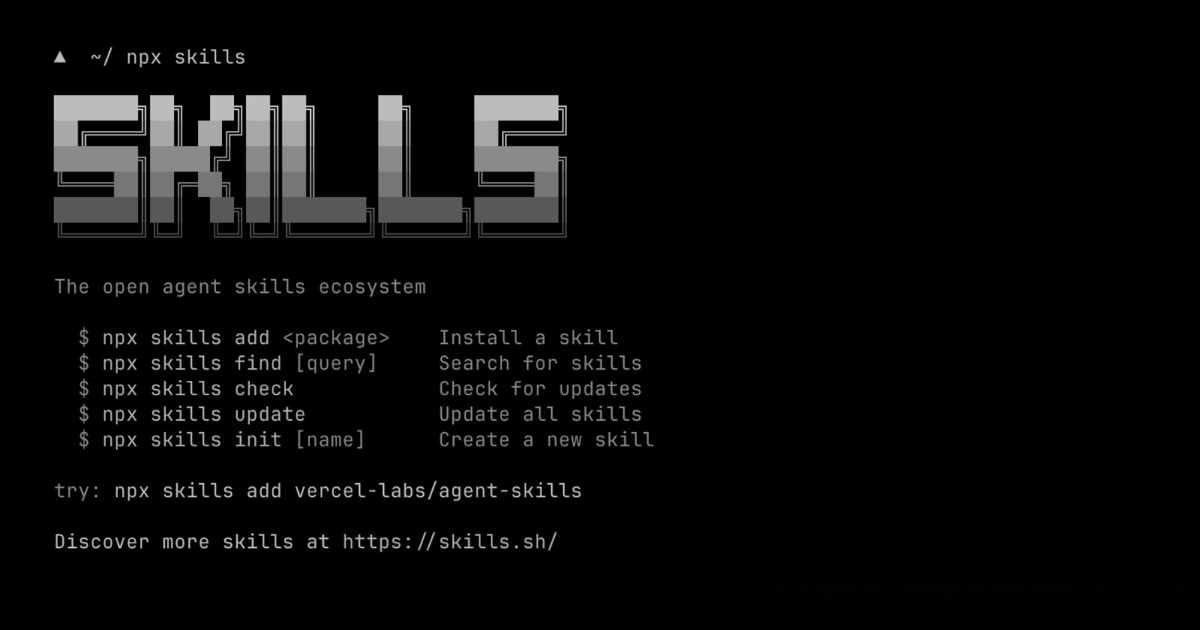
Vercel has released Skills.sh, an open-source tool designed to provide AI agents with a standardized way to execute reusable actions, or skills, through the command line.
By Daniel DominguezAgent Trace: Cursor Proposes an Open Specification for AI Code Attribution
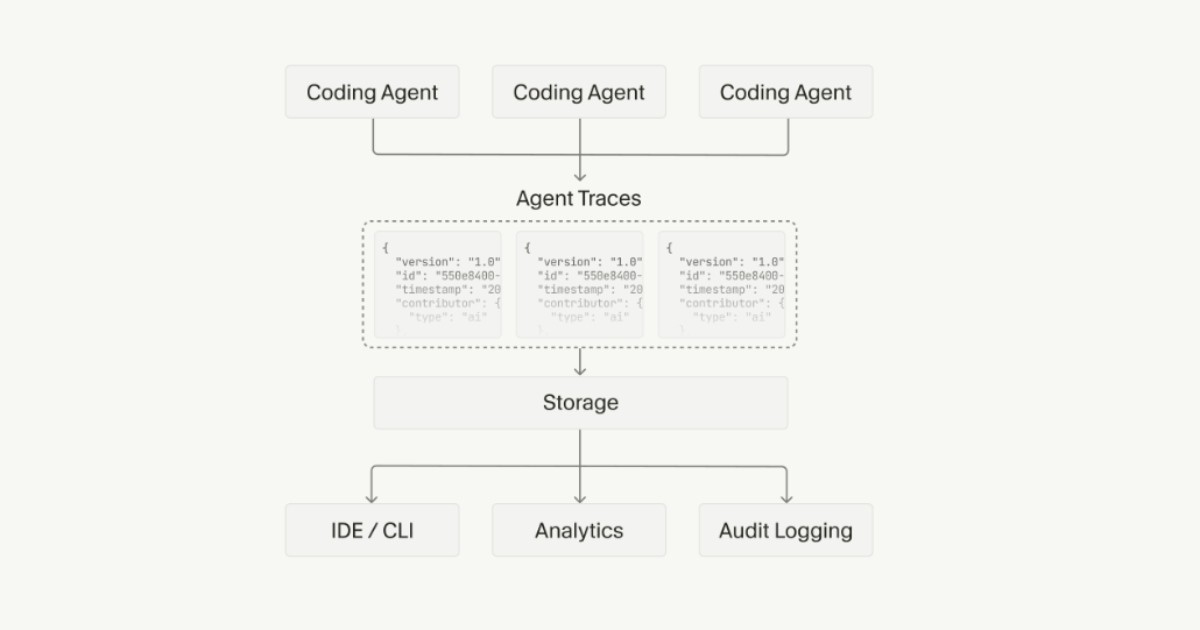
Cursor has published Agent Trace, a draft open specification aimed at standardizing how AI-generated code is attributed in software projects. Released as a Request for Comments (RFC), the proposal defines a vendor-neutral format for recording AI contributions alongside human authorship in version-controlled codebases.
By Robert KrzaczyńskiArticle: From Alert Fatigue to Agent-Assisted Intelligent Observability

As systems grow, observability becomes harder to maintain and incidents harder to diagnose. Agentic observability layers AI on existing tools, starting in read-only mode to detect anomalies and summarize issues. Over time, agents add context, correlate signals, and automate low-risk tasks. This approach frees engineers to focus on analysis and judgment.
By Rohit Dhawan
© 2026 Created by Michael Levin.
Powered by
![]()