Codetown
Codetown ::: a software developer's community
What's the difference between Grid computing and Cloud Computing
I don't clearly catch the difference betwenn these two concept. Someone told me that the essential différence is that the cloud computing give you a large space of storage and the grig give more advantages than storage, we can profit to much power with this last.
Does any one know more clearly these two concept; and tell us?
Tags:
Replies to This Discussion
-
Permalink Reply by Thomas Michaud on October 26, 2011 at 3:38pm
-
I don't claim to be the expert, but the difference is (I think) in use.
Grid represents a scalable framework. You write your algorithm and your code and use as much computing power as you wallet can afford. (Useful as some work can be highly parallelizable) .
Cloud computing offers storage (true) but it's also represents the applications as well. Ideally with cloud computing, you don't need to have certain applications on your desktop - as long as you can hit the cloud, you can get, update, and use your data.
-
-
Permalink Reply by Hervé-greg MOKWABO on October 26, 2011 at 3:49pm
-
Thanks thomas;
What I got :
Grid - much computing power and can be highly parallelizable
Cloud - Storage and dont need to have certain applications on your desktop ( that's just like server application?)
Someone can tell us more?
-
-
Permalink Reply by Bradlee Sargent on October 27, 2011 at 10:58pm
-
I think if you look at the history, you will understand some difference.
In my own experience, the grid began with Oracle using it as a type of metadatabase, which would point to multiple databases residing on different but uniform hardware systems. So if a company had multiple unix boxes and needed to increase the size of their database, instead of purchasing additional hardware they could implement the grid database and combine their multiple unix servers into one database resource.
Cloud is much more in terms of it offering not only a database, but also an entire server including the operating system.
The cloud exposes an operating system, whereas a grid exposes a database.
But I am no buzz word expert so I might be wrong.
-
-
Permalink Reply by Jackie Gleason on October 28, 2011 at 10:17am
-
I just talked to a buddy about this, essentially the Oracle Grid product is differant because it runs the DB in memory. So access times are a lot quicker. I don't think it is really a matter of Vs. so much as Grid computing is a way to handle db transactions in a faster way.
He said their grid servers had something like 72gbs of ram. Freaking crazy
-
-
Permalink Reply by Hervé-greg MOKWABO on November 29, 2011 at 10:33am
-
Please Bradley, wha do you think about Jackie's reaction?
-
Notes
Welcome to Codetown!
 Codetown is a social network. It's got blogs, forums, groups, personal pages and more! You might think of Codetown as a funky camper van with lots of compartments for your stuff and a great multimedia system, too! Best of all, Codetown has room for all of your friends.
Codetown is a social network. It's got blogs, forums, groups, personal pages and more! You might think of Codetown as a funky camper van with lots of compartments for your stuff and a great multimedia system, too! Best of all, Codetown has room for all of your friends.
Created by Michael Levin Dec 18, 2008 at 6:56pm. Last updated by Michael Levin May 4, 2018.
Looking for Jobs or Staff?
Check out the Codetown Jobs group.
InfoQ Reading List
Google Researchers Propose Bayesian Teaching Method for Large Language Models
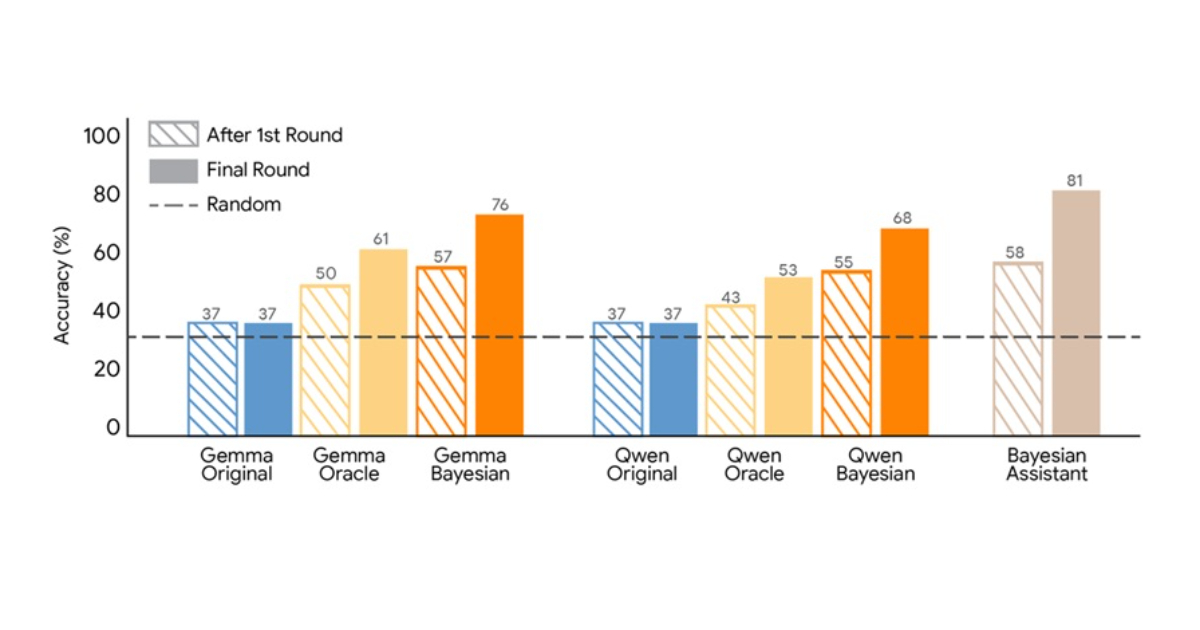
Google Research has proposed a training method that teaches large language models to approximate Bayesian reasoning by learning from the predictions of an optimal Bayesian system. The approach focuses on improving how models update beliefs as they receive new information during multi-step interactions.
By Daniel DominguezCloudflare Introduces Support for ASPA, an Emerging Internet Routing Security Standard

Cloudflare recently announced support for ASPA (Autonomous System Provider Authorization). The new cryptographic standard helps make Internet routing safer by verifying the path data takes across networks to reach its destination and preventing traffic from traversing unreliable or untrusted networks.
By Renato LosioDoorDash Builds LLM Conversation Simulator to Test Customer Support Chatbots at Scale
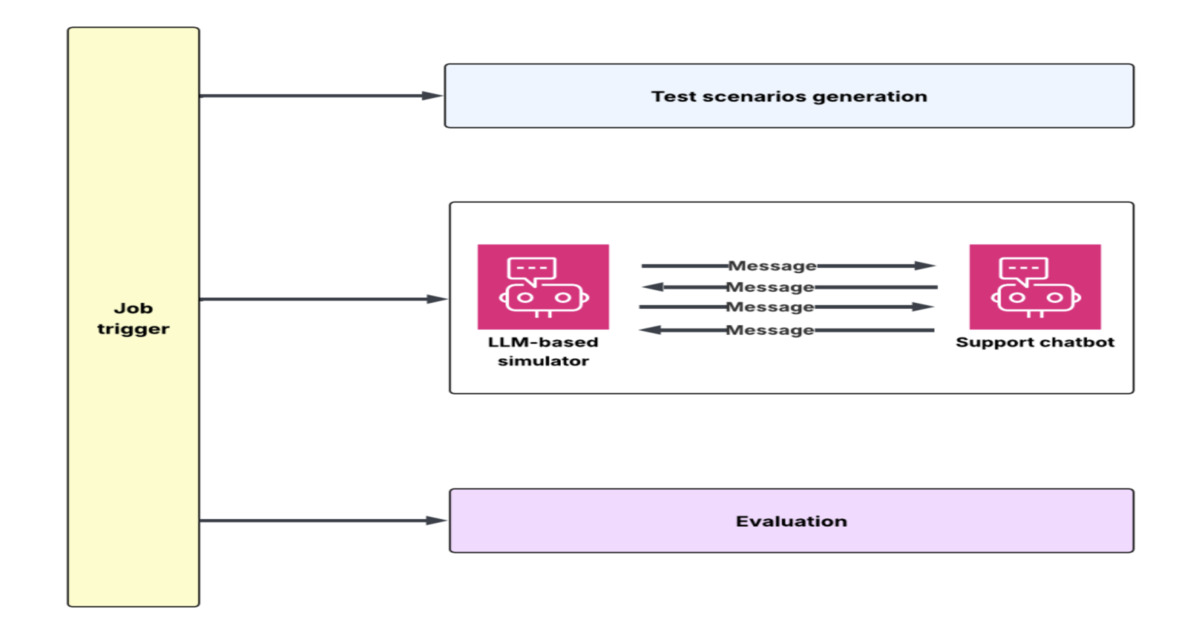
DoorDash engineers built a simulation and evaluation flywheel to test large language model customer support chatbots at scale. The system generates multi-turn synthetic conversations using historical transcripts and backend mocks, evaluates outcomes with an LLM-as-judge framework, and enables rapid iteration on prompts, context, and system design before production deployment.
By Leela KumiliNetflix Uncovers Kernel-Level Bottlenecks While Scaling Containers on Modern CPUs

Engineers at Netflix have uncovered deep performance bottlenecks in container scaling that trace not to Kubernetes or containerd alone, but into the CPU architecture and Linux kernel itself.
By Craig RisiPresentation: Beyond the Code: Hiring for Cultural Alignment

Alicia Collymore discusses the critical role of cultural alignment in building high-performing engineering teams. She explains how to move beyond "vibes" by identifying specific attributes in company values and assessing them during coding challenges and system design sessions. She shares practical advice on using interview debriefs, assessment criteria, and "culture add" to drive growth.
By Alicia Collymore
© 2026 Created by Michael Levin.
Powered by
![]()