Codetown
Codetown ::: a software developer's community
Hot New Language (Groovy)
Slightly modified from original post: http://adamldavis.com/
There’s a hot new programming language that I’m excited about. It can be used dynamically or statically-typed, your choice. It supports functional programming constructs, including first-class functions, currying, and more. It has multiple-inheritance, type inference, and meta-programming. It also integrates really well with a battle-tested enterprise-worthy language and best-of-class virtual machine.
This programming language actually isn’t that new. It’s from 2004, but they’ve recently added a lot of new features, such as traits. Oh, did I mention it has a great community and tons of frameworks built on top of it for web-applications, testing, and even full build systems. This language is great for building DSL’s and is very light-weight. Oh, and it can be compiled to JavaScript and it can be used to develop for Android.
As you might have guessed, this language is called “Groovy”. The virtual machine it’s built on is the JVM, the web framework is Grails, the testing framework is spock, and the build system is Gradle.
As you may have heard, Pivotal has dropped its Groovy/Grails support. Although some will take this news as sky-falling bad news, I actually think it’s the opposite. Pivotal only "acquired" the developers behind Groovy and Grails through a “Russian nesting doll” turn of events. In short, SpringSource bought G2One then Pivotal bought SpringSource (and VMWare goes in there somewhere).
There are tons of companies that stand to benefit from Groovy that could take up its funding: Google, Oracle, and Gradleware come to mind.
Groovy has a lot going for it. With projects like ratpack, grooscript, gradle, and others, its future looks bright.
Also: Grails has improved dramatically and will support microservices much better in the next release (3) among other improvements.
Update: Groovy Moving to a Foundation
Comment
-
Comment by Jackie Gleason on April 24, 2015 at 9:27am
-
In my world people aren't letting the news worry them too much. No plans to switch back to spring but I do think this highlights one of the weaknesses of Groovy. It is a lot harder to convert a Groovy file into a Java file than the reverse.
-
Comment by Adam Davis on March 5, 2015 at 4:47pm
-
Update: Groovy stewardship is moving to the Apache Software Foundation.
Here's a great article by Cédric Champeau (one of the developers behind Groovy) on Groovy's history and who has contributed to it over the years: http://melix.github.io/blog/2015/02/who-is-groovy.html
-
Comment by Adam Davis on March 1, 2015 at 9:56am
-
Clarification: Groovy and Grails are open-source projects. I used the short-hand "acquired" to describe Pivotal's hiring of the developers behind Groovy and Grails. Groovy and Grails development would continue even if no one hires these developers, just at a slower pace.
Notes
Welcome to Codetown!
 Codetown is a social network. It's got blogs, forums, groups, personal pages and more! You might think of Codetown as a funky camper van with lots of compartments for your stuff and a great multimedia system, too! Best of all, Codetown has room for all of your friends.
Codetown is a social network. It's got blogs, forums, groups, personal pages and more! You might think of Codetown as a funky camper van with lots of compartments for your stuff and a great multimedia system, too! Best of all, Codetown has room for all of your friends.
Created by Michael Levin Dec 18, 2008 at 6:56pm. Last updated by Michael Levin May 4, 2018.
Looking for Jobs or Staff?
Check out the Codetown Jobs group.
InfoQ Reading List
Google Researchers Propose Bayesian Teaching Method for Large Language Models
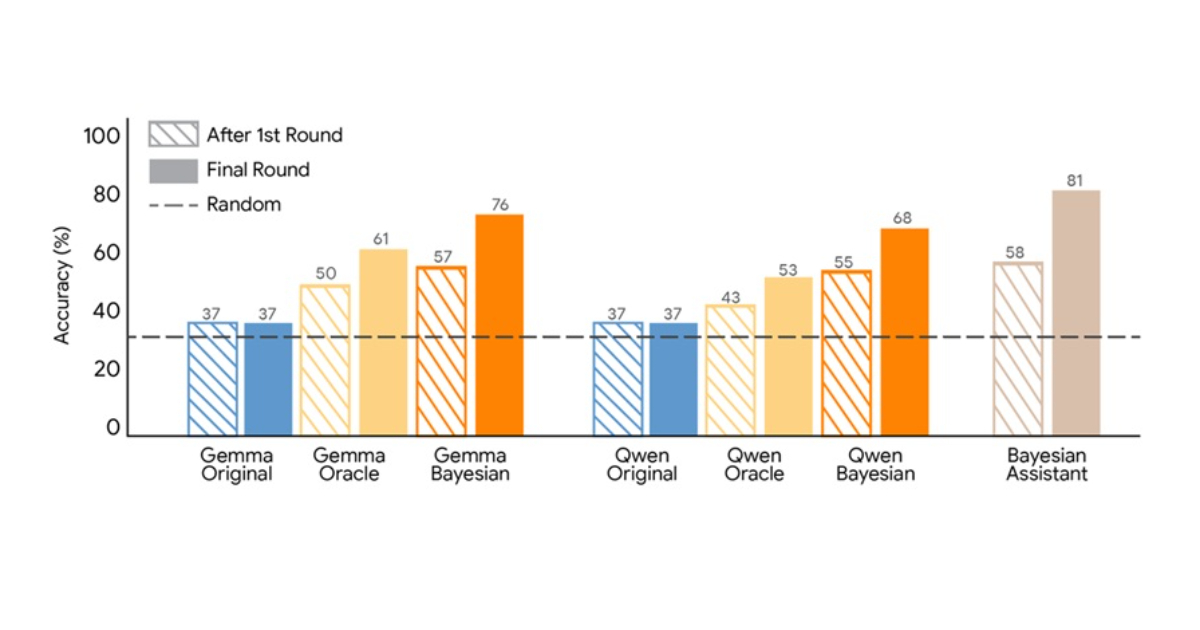
Google Research has proposed a training method that teaches large language models to approximate Bayesian reasoning by learning from the predictions of an optimal Bayesian system. The approach focuses on improving how models update beliefs as they receive new information during multi-step interactions.
By Daniel DominguezCloudflare Introduces Support for ASPA, an Emerging Internet Routing Security Standard

Cloudflare recently announced support for ASPA (Autonomous System Provider Authorization). The new cryptographic standard helps make Internet routing safer by verifying the path data takes across networks to reach its destination and preventing traffic from traversing unreliable or untrusted networks.
By Renato LosioDoorDash Builds LLM Conversation Simulator to Test Customer Support Chatbots at Scale
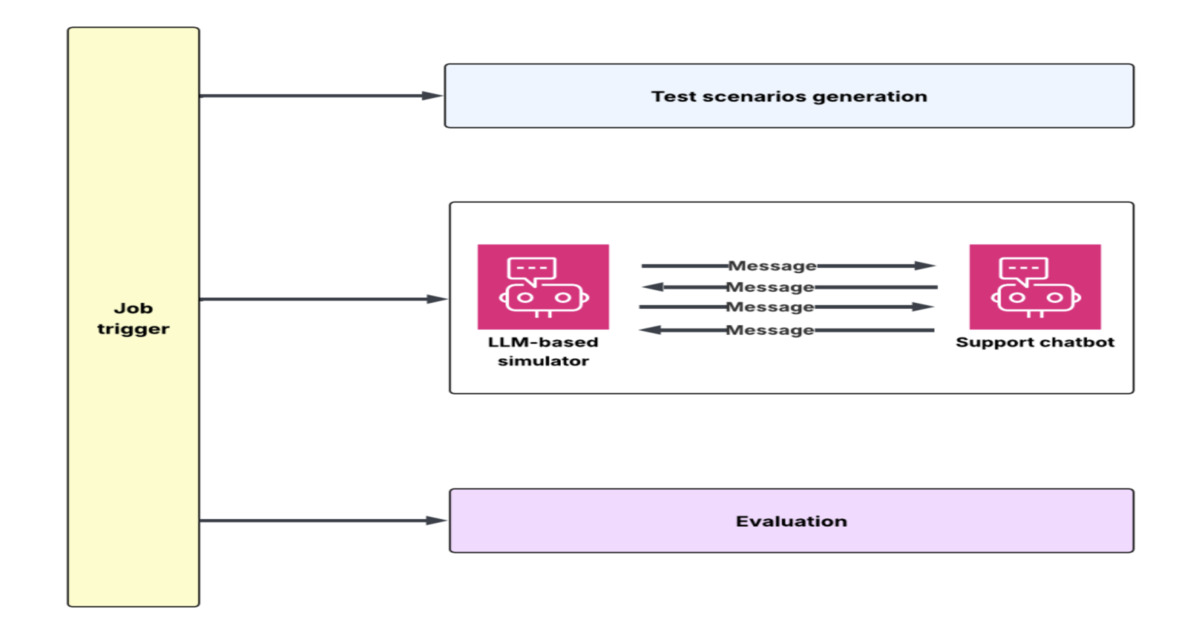
DoorDash engineers built a simulation and evaluation flywheel to test large language model customer support chatbots at scale. The system generates multi-turn synthetic conversations using historical transcripts and backend mocks, evaluates outcomes with an LLM-as-judge framework, and enables rapid iteration on prompts, context, and system design before production deployment.
By Leela KumiliNetflix Uncovers Kernel-Level Bottlenecks While Scaling Containers on Modern CPUs

Engineers at Netflix have uncovered deep performance bottlenecks in container scaling that trace not to Kubernetes or containerd alone, but into the CPU architecture and Linux kernel itself.
By Craig RisiPresentation: Beyond the Code: Hiring for Cultural Alignment

Alicia Collymore discusses the critical role of cultural alignment in building high-performing engineering teams. She explains how to move beyond "vibes" by identifying specific attributes in company values and assessing them during coding challenges and system design sessions. She shares practical advice on using interview debriefs, assessment criteria, and "culture add" to drive growth.
By Alicia Collymore
© 2026 Created by Michael Levin.
Powered by
![]()
You need to be a member of Codetown to add comments!
Join Codetown