Codetown
Codetown ::: a software developer's community
Kotlin Thursdays - Introduction to Functional Programming Part 2
Resources
- Higher-Order Functions and Lambdas:https://kotlinlang.org/docs/reference/lambdas.html
- FP in Kotlin Part 1: https://medium.com/kotlin-thursdays/functional-programming-in-kotli...
Introduction
Last week, we went over higher order functions in Kotlin. We learned how higher order functions can accept functions as parameters and are also able to return functions. This week, we will take a look at lambdas. Lambdas are another type of function and they are very popular in the functional programming world.
Logic & Data
Computer programs are made up of two parts: logic and data. Usually, logic is described in functions and data is passed to those functions. The functions do things with the data, and return a result. When we write a function we would typically create a named function. As we saw last week, this is a typical named function:
fun hello(name: String): String {
return "Hello, $name"
}
Then you can call this function:
fun main() {
println(hello("Matt"))
}
Which gives us the result:
Hello, Matt
Functions as Data
There is a concept in the functional programming world where functions are treated as data. Lambdas (functions as data) can do the same thing as named functions, but with lambdas, the content of a given function can be passed directly into other functions. A lambda can also be assigned to a variable as though it were just a value.
Lambda Syntax
Lambdas are similar to named functions but lambdas do not have a name and the lambda syntax looks a little different. Whereas a function in Kotlin would look like this:
fun hello() {
return "Hello World"
}
The lambda expression would look like this:
{ "Hello World" }
Here is an example with a parameter:
fun(name: String) {
return "Hello, ${name}"
}
The lambda version:
{ name: String -> "Hello, $name" }
You can call the lambda by passing the parameter to it in parentheses after the last curly brace:
{ name: String -> "Hello, $name" }("Matt")
It’s also possible to assign a lambda to a variable:
val hello = { name: String -> "Hello, $name" }
You can then call the variable the lambda has been assigned to, just as if it was a named function:
hello("Matt")
Lambdas provide us with a convenient way to pass logic into other functions without having to define that logic in a named function. This is very useful when processing lists or arrays of data. We’ll take a look at processing lists with lambdas in the next post!
Tags:
Replies to This Discussion
Notes
Welcome to Codetown!
 Codetown is a social network. It's got blogs, forums, groups, personal pages and more! You might think of Codetown as a funky camper van with lots of compartments for your stuff and a great multimedia system, too! Best of all, Codetown has room for all of your friends.
Codetown is a social network. It's got blogs, forums, groups, personal pages and more! You might think of Codetown as a funky camper van with lots of compartments for your stuff and a great multimedia system, too! Best of all, Codetown has room for all of your friends.
Created by Michael Levin Dec 18, 2008 at 6:56pm. Last updated by Michael Levin May 4, 2018.
Looking for Jobs or Staff?
Check out the Codetown Jobs group.
InfoQ Reading List
DoorDash Builds LLM Conversation Simulator to Test Customer Support Chatbots at Scale
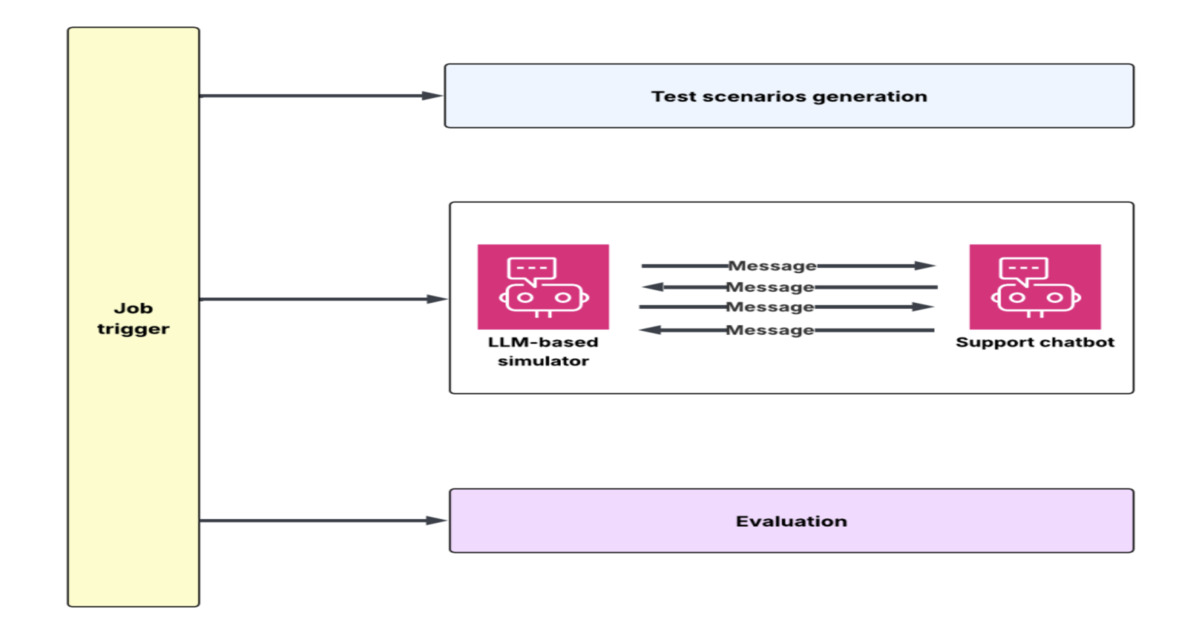
DoorDash engineers built a simulation and evaluation flywheel to test large language model customer support chatbots at scale. The system generates multi-turn synthetic conversations using historical transcripts and backend mocks, evaluates outcomes with an LLM-as-judge framework, and enables rapid iteration on prompts, context, and system design before production deployment.
By Leela KumiliNetflix Uncovers Kernel-Level Bottlenecks While Scaling Containers on Modern CPUs

Engineers at Netflix have uncovered deep performance bottlenecks in container scaling that trace not to Kubernetes or containerd alone, but into the CPU architecture and Linux kernel itself.
By Craig RisiPresentation: Beyond the Code: Hiring for Cultural Alignment

Alicia Collymore discusses the critical role of cultural alignment in building high-performing engineering teams. She explains how to move beyond "vibes" by identifying specific attributes in company values and assessing them during coding challenges and system design sessions. She shares practical advice on using interview debriefs, assessment criteria, and "culture add" to drive growth.
By Alicia CollymoreArticle: The Oil and Water Moment in AI Architecture

Have you ever tried mixing oil and water? That is the moment software architecture is entering as deterministic systems meet non deterministic AI behaviour. Architects must anchor intelligent systems in intent, governance and systems thinking. This article introduces the Architect’s V Impact Canvas, a framework for navigating this shift while keeping human trust at the centre.
By Shweta VohraPodcast: Information Flow: The Hidden Driver of Engineering Culture

In this podcast, Shane Hastie, Lead Editor for Culture & Methods, spoke to Adrian Peryer about Ron Westrum's organizational culture continuum, the role of information flow in shaping team culture, and how leaders can develop requisite imagination to detect weak signals.
By Adrian Peryer
© 2026 Created by Michael Levin.
Powered by
![]()