Codetown
Codetown ::: a software developer's community
Are you interested in learning about graph databases? The folks at Neo4J published a book and it's free! Here's a link to the download page: http://graphdatabases.com/
Tags:
Replies to This Discussion
-
Permalink Reply by Juan Rolando Reza on March 16, 2015 at 4:45pm
-
Database representation of graph-structured information is fascinating in its own right.
I have been studying genomics technology in which graphs play a big role, both as information-structure that is the basis of certain algorithms, as well as the data driving visualizations or visually-interesting real-world structures.
As an example, here is a visualization of a protein complex that catches the eye.
See http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/FOXP2#/media/File:Protein_FOXP2_PDB_2a...
The image is a Richardson diagram which is (mostly) automatically generated from a database describing the molecular structure of the protein. This type of diagram was invented (i.e. originally hand-drawn) by Jane Richardson, PhD.
I wonder if the book "Graph Databases" touches on this.
Presently, I am doing a research study on a particular feature of the epigenome. It involves large DNA databases (actually, structured flat files), elaborate algorithms for sequence correlation, and histone complexes. Each of these involves graph-theoretic representations and inference functions from graph structures.
The "databases" I know for DNA, the transcriptome, pathways, etc. do not lend themselves to conventional SQL, or even noSQL as far as I know to date. (Chime in anyone? )
I will be presenting a paper at the IEEE SouthCon conference in April 2015 which touches on a graph-theoretic feature of certain (sequencing) problems lending itself to massively-parallel-ization of linearly-expressable algorithms.
I am pleased to see a free book on graph databases. Thanks!
-
Notes
Welcome to Codetown!
 Codetown is a social network. It's got blogs, forums, groups, personal pages and more! You might think of Codetown as a funky camper van with lots of compartments for your stuff and a great multimedia system, too! Best of all, Codetown has room for all of your friends.
Codetown is a social network. It's got blogs, forums, groups, personal pages and more! You might think of Codetown as a funky camper van with lots of compartments for your stuff and a great multimedia system, too! Best of all, Codetown has room for all of your friends.
Created by Michael Levin Dec 18, 2008 at 6:56pm. Last updated by Michael Levin May 4, 2018.
Looking for Jobs or Staff?
Check out the Codetown Jobs group.
InfoQ Reading List
How Datadog Cut the Size of Its Agent Go Binaries by 77%

After the Datadog Agent grew from 428 MiB to 1.22 GiB over a period of 5 years, Datadog engineers set out to reduce its binary size. They discovered that most Go binary bloat comes from hidden dependencies, disabled linker optimizations, and subtle behaviors in the Go compiler and linker.
By Sergio De SimoneGitLab Suggests AI Can Detect Vulnerabilities But it's AI Governance that Determines Risk

Artificial intelligence is rapidly transforming how software vulnerabilities are detected, but questions about who governs the risks AI exposes, and how those risks are acted on, are becoming increasingly urgent, according to a new blog post by GitLab.
By Craig RisiCloudflare Releases Experimental Next.js Alternative Built With AI Assistance

Cloudflare released vinext, an experimental Next.js reimplementation built on Vite by one engineer, with AI guidance over one week, for $1,100. Early benchmarks show 4.4x faster builds, but Cloudflare cautions it's untested at scale. Missing static pre-rendering. HN reaction skeptical, noting Vite does the heavy lifting. Already running on CIO.gov despite experimental status.
By Steef-Jan WiggersNetflix Automates RDS PostgreSQL to Aurora PostgreSQL Migration Across 400 Production Clusters
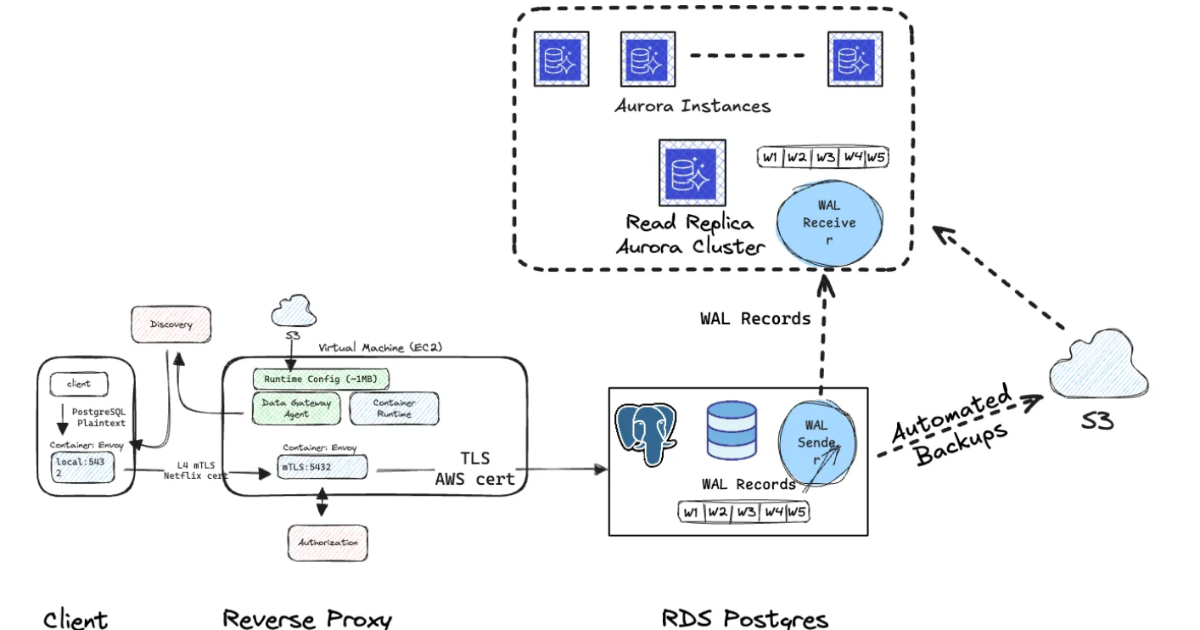
Netflix engineers describe an internal automation platform that migrates nearly 400 RDS PostgreSQL clusters to Aurora, reducing downtime and operational risk. The platform coordinates replication, CDC handling, controlled cutover, and rollback, while supporting service teams in a self-service migration workflow.
By Leela KumiliPresentation: 4 Patterns of AI Native Development
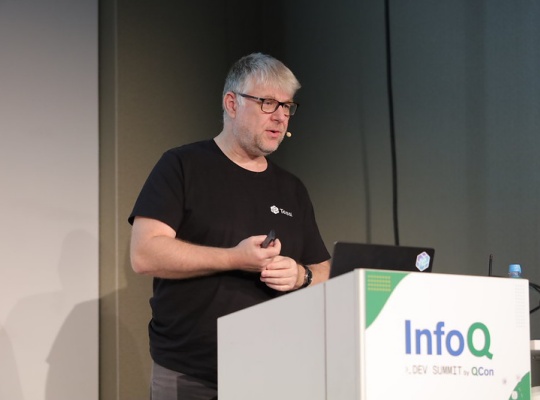

Patrick Debois discusses the evolution of software engineering in the age of AI. He shares four key patterns: transitioning from producer to manager, focusing on intent over implementation through spec-driven development, moving from delivery to discovery, and managing agentic knowledge. He explains how these shifts redefine seniority, team roles, and the future of the DevOps workflow.
By Patrick Debois
© 2026 Created by Michael Levin.
Powered by
![]()