Codetown
Codetown ::: a software developer's community
Meeting Mycroft: An Open AI Platform You Can Order Around By Voice
Mycroft developer Ryan Sipes, speaking from the show floor of this year's OSCON in Austin, Texas...
(see our video interview here), says that what started out as a weekend project to use voice input and some light AI to locate misplaced tools in a makerspace morphed into a much more ambitious, and successfully crowd-funded, project -- hosted at the Lawrence Center for Entrepreneurship in Lawrence, Kansas -- when he and his fellow developers realized that the state of speech recognition and interfaces to exploit it were in a much more rudimentary state than they initially assumed.
How ambitious? Mycroft bills itself as "an open hardware artificial intelligence platform"; the goal is to allow you to "interact with everything in your house, and interact with all your data, through your voice." That's a familiar aim of late, but mostly from a shortlist of the biggest names in technology. Apple's Siri is exclusive to (and helps sell) Apple hardware; Google's voice interface likewise sells Android phones and tablets, and helps round out Google's apps-and-interfaces-for-everything approach. Amazon and Microsoft have poured resources into voice recognition systems, too -- Amazon's Echo, running the company's Alexa voice service, is probably the most direct parallel to the Mycroft system that was on display at OSCON, in that it provides a dedicated box loaded with mics and a speaker system for 2-way voice interaction.
The Mycroft system, though, is based on two of the first names in open hardware -- Raspberry Pi and Arduino -- and it's meant to be and stay open; all of its software is released under GPL v3. The initial hardware for Mycroft includes RCA ports, as well as an ethernet jack, 4 USB ports, HDMI, and dozens of addressable LEDs that form Mycroft's "face." That HDMI output might not be immediately useful, but Sipes points out that the the hardware is powerful enough to play Netflix films, or multimedia software like Kodi, and to control them by voice. Unusually for a consumer device, even one aimed at hardware hackers, Mycroft also includes an accessible ribbon-cable port, for users who'd like to hook up a camera or some other peripheral. Two other "ports" (of a sort) might appeal to just those kind of users, too: if you pop out the plugs emblazoned with the OSI Open Hardware logo, two holes on each side of Mycroft's case facilitate adding it to a robot body or other mounting system.
The open-source difference in Mycroft isn't just in the hacker-friendly hardware. The real star of the show is the software (Despite the hardware on offer, "We're a software company," says Sipes), and that's proudly open as well. The Python-based project is drawing on, and creating, open source back-end tools, but not tied to any particular back-end for interpreting or acting on the voice input it receives. The team has open sourced several tools so far: the Adapt intent parser, text-to-speech engine Mimic (based on a fork of CMU's Flite), and open speech-to-text engine OpenSTT.
The commercial projects named above (Siri, et al) may offer various degrees of privacy or extensibility, but ultimately they all come from "large companies that work really hard to mine your data" and to keep each user in a silo, says Sipes. By contrast, "We're like Switzerland." With Mycroft the speech recognition and speech synthesis tools are swappable, and there's an active dev community adding new voice-activated capabilities ("skills") to the system.
And if you can program Python, your idea could be next.
Notes
Welcome to Codetown!
 Codetown is a social network. It's got blogs, forums, groups, personal pages and more! You might think of Codetown as a funky camper van with lots of compartments for your stuff and a great multimedia system, too! Best of all, Codetown has room for all of your friends.
Codetown is a social network. It's got blogs, forums, groups, personal pages and more! You might think of Codetown as a funky camper van with lots of compartments for your stuff and a great multimedia system, too! Best of all, Codetown has room for all of your friends.
Created by Michael Levin Dec 18, 2008 at 6:56pm. Last updated by Michael Levin May 4, 2018.
Looking for Jobs or Staff?
Check out the Codetown Jobs group.
InfoQ Reading List
Cloudflare Introduces Support for ASPA, an Emerging Internet Routing Security Standard

Cloudflare recently announced support for ASPA (Autonomous System Provider Authorization). The new cryptographic standard helps make Internet routing safer by verifying the path data takes across networks to reach its destination and preventing traffic from traversing unreliable or untrusted networks.
By Renato LosioDoorDash Builds LLM Conversation Simulator to Test Customer Support Chatbots at Scale
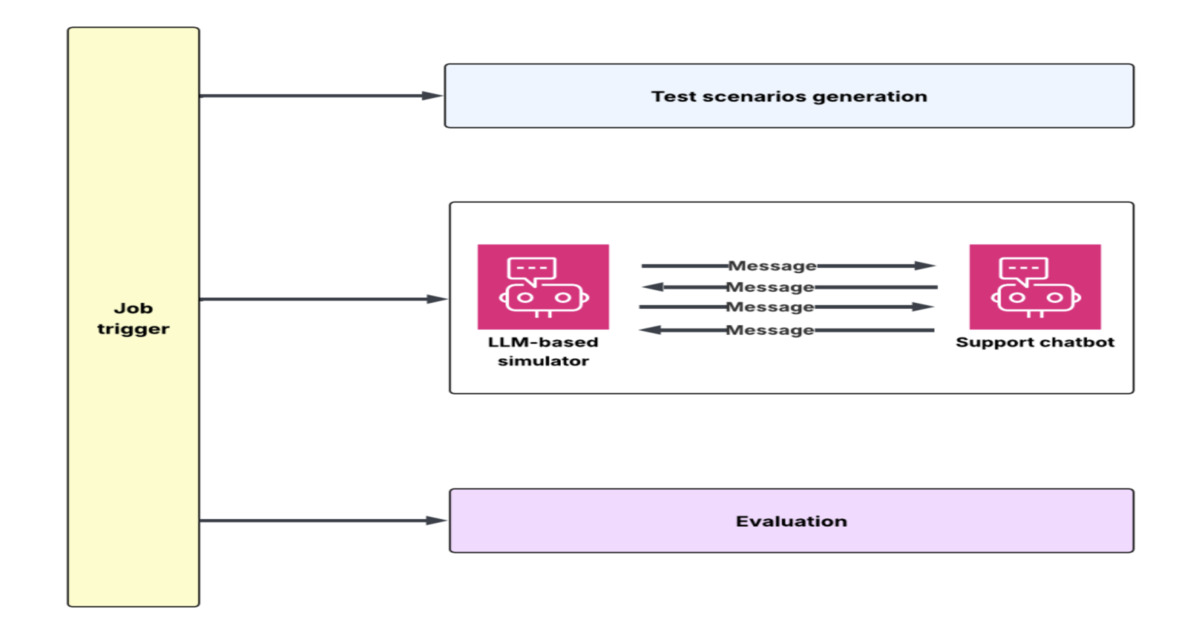
DoorDash engineers built a simulation and evaluation flywheel to test large language model customer support chatbots at scale. The system generates multi-turn synthetic conversations using historical transcripts and backend mocks, evaluates outcomes with an LLM-as-judge framework, and enables rapid iteration on prompts, context, and system design before production deployment.
By Leela KumiliNetflix Uncovers Kernel-Level Bottlenecks While Scaling Containers on Modern CPUs

Engineers at Netflix have uncovered deep performance bottlenecks in container scaling that trace not to Kubernetes or containerd alone, but into the CPU architecture and Linux kernel itself.
By Craig RisiPresentation: Beyond the Code: Hiring for Cultural Alignment

Alicia Collymore discusses the critical role of cultural alignment in building high-performing engineering teams. She explains how to move beyond "vibes" by identifying specific attributes in company values and assessing them during coding challenges and system design sessions. She shares practical advice on using interview debriefs, assessment criteria, and "culture add" to drive growth.
By Alicia CollymoreArticle: The Oil and Water Moment in AI Architecture

Have you ever tried mixing oil and water? That is the moment software architecture is entering as deterministic systems meet non deterministic AI behaviour. Architects must anchor intelligent systems in intent, governance and systems thinking. This article introduces the Architect’s V Impact Canvas, a framework for navigating this shift while keeping human trust at the centre.
By Shweta Vohra
© 2026 Created by Michael Levin.
Powered by
![]()
You need to be a member of Codetown to add comments!
Join Codetown